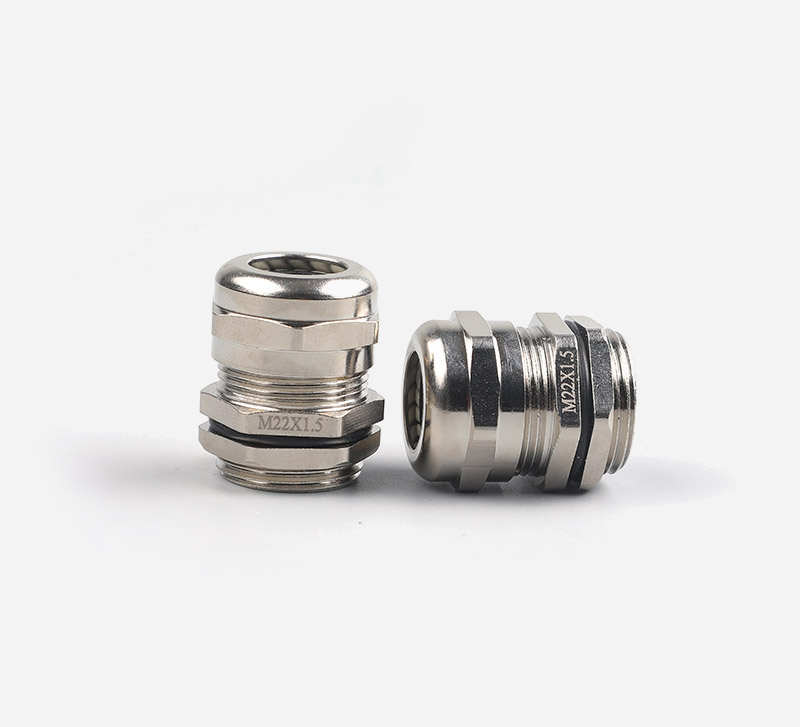
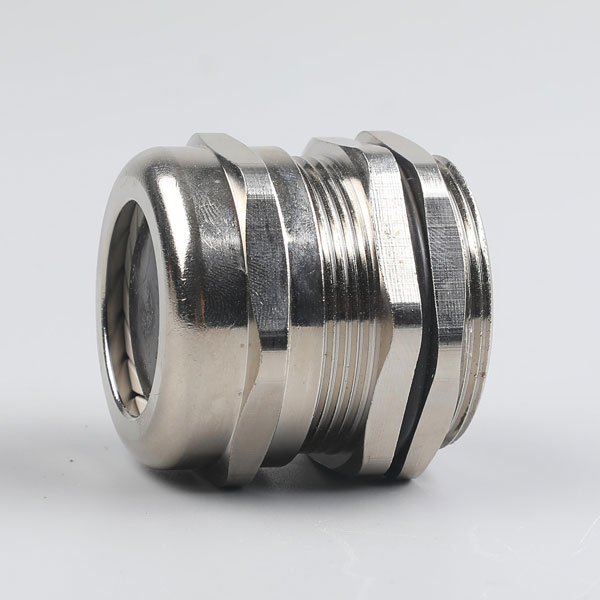
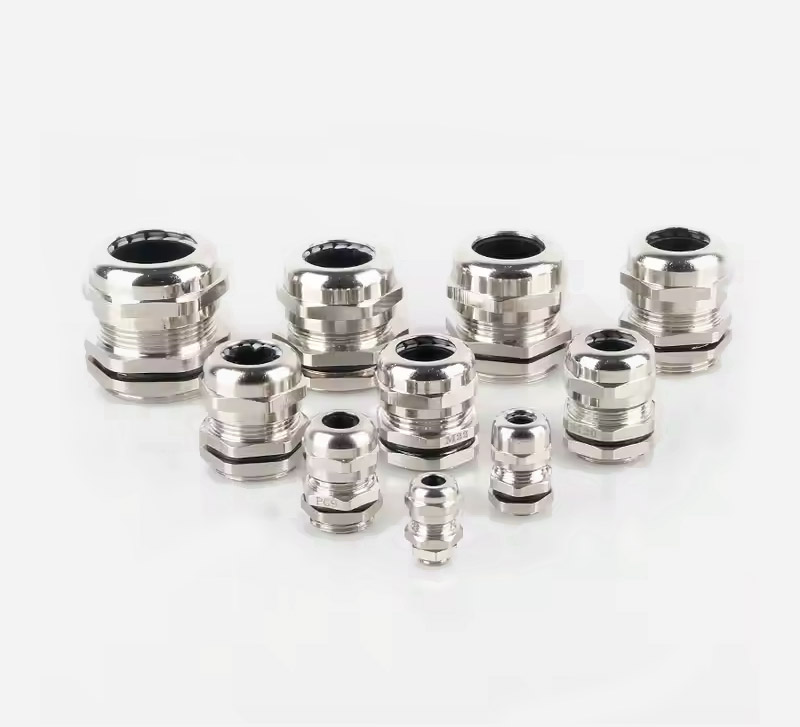
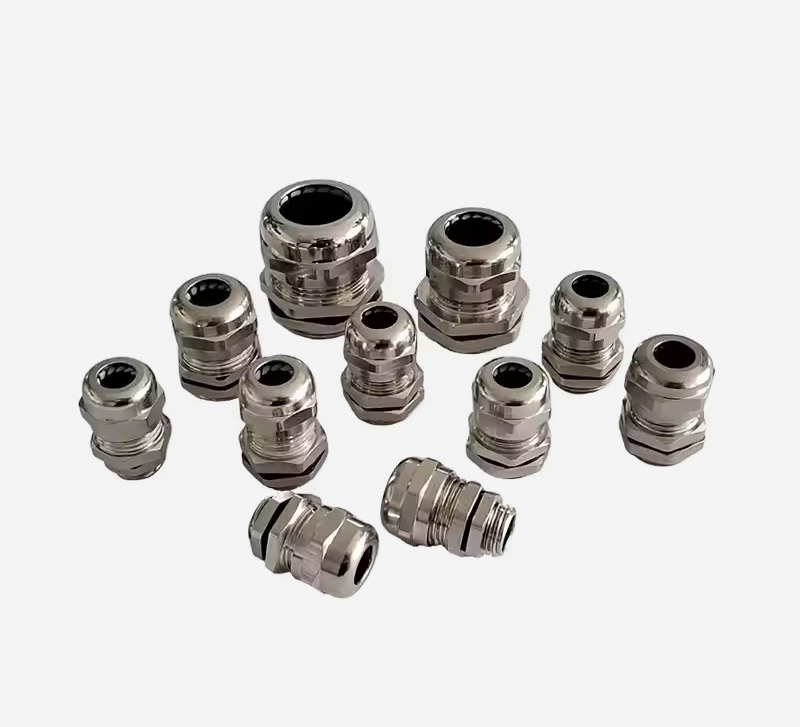
This marine-grade waterproof cable gland combines premium stainless steel construction with metric thread standards, delivering exceptional performance in extreme environments. Engineered for high temperature operations and corrosive conditions, it ensures secure cable management in offshore, chemical processing, and industrial automation applications.
Core Material Advantages
• High Temp Resistant Stainless Steel: SS composition maintains structural integrity in -50°C to 100°C environments.
• Triple Protection System: Combines acid/alkali resistance + saltwater corrosion resistance + high temperature oxidation resistance.
• Durability: 30% higher tensile strength than standard stainless steel glands.
Industrial Applications
✓ High Temp Manufacturing: Foundries, glass plants, thermal power stations.
✓ Marine & Offshore: Subsea equipment, drilling platform cable routing.
✓ Chemical Processing: Reactor vessel connections, acid storage facilities.
✓ Automotive: Engine compartment wiring, EV battery thermal management.
Maintenance Advantage
Requires 68% less maintenance than brass counterparts in high temp humid environments.
Integrated anti-vibration design prevents thread loosening under thermal expansion.