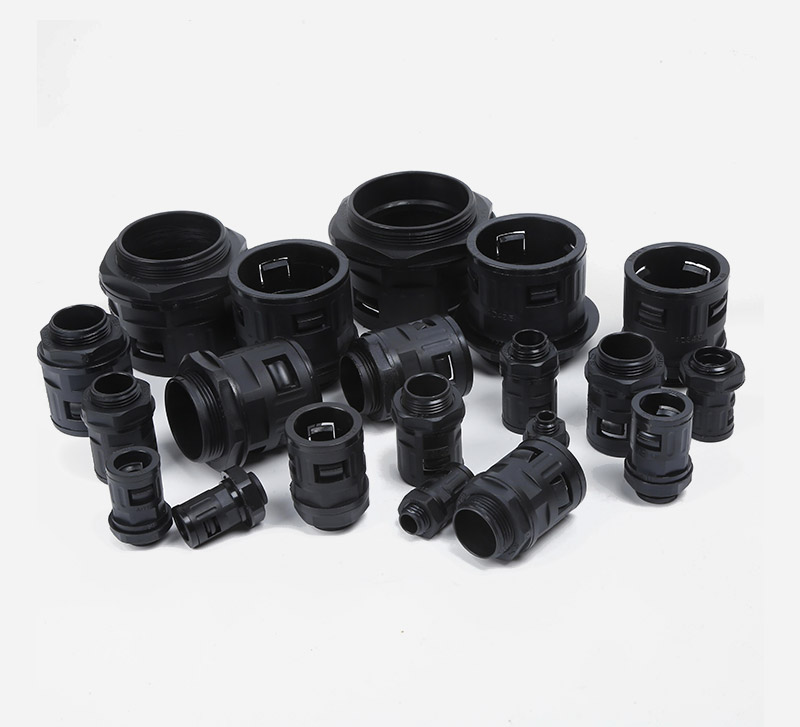
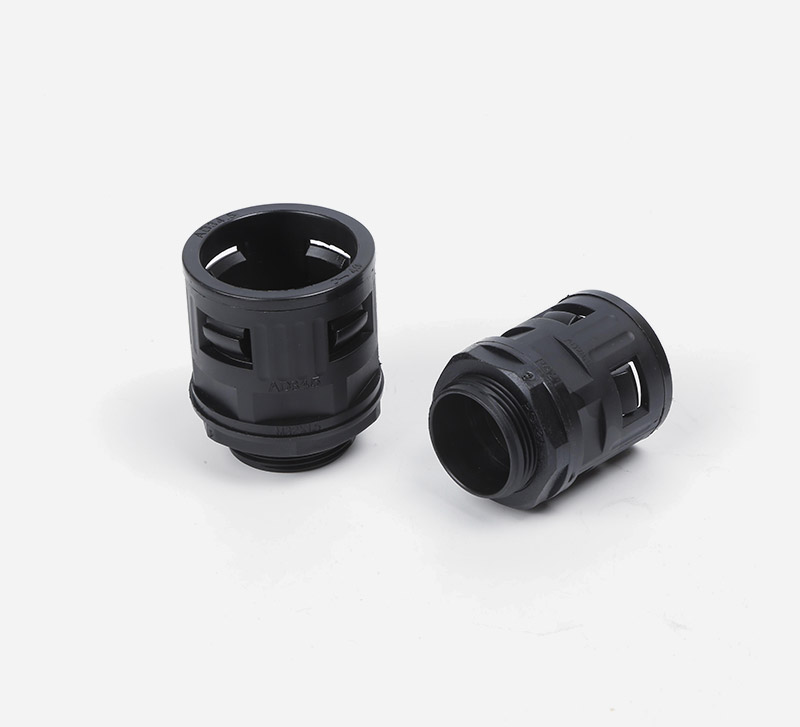
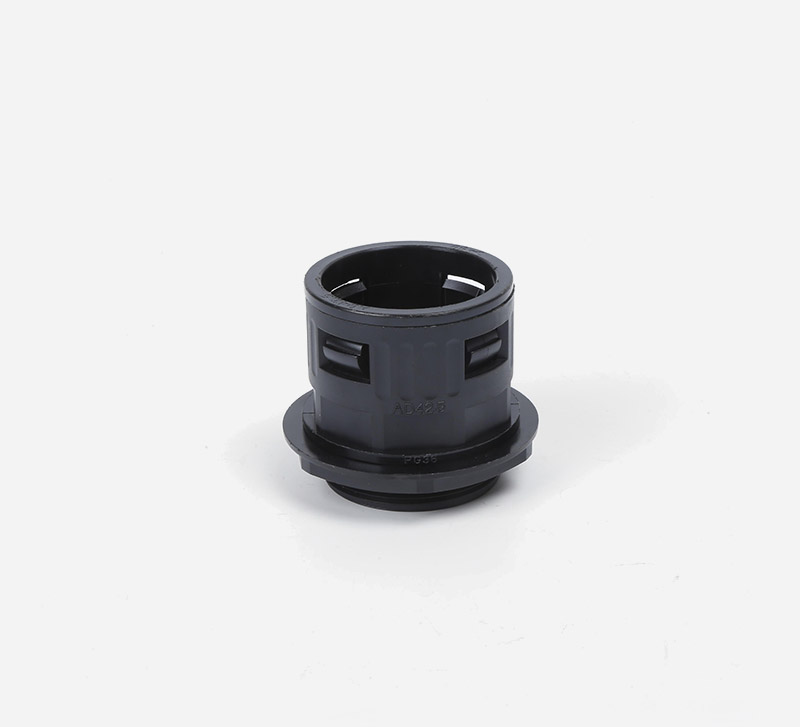
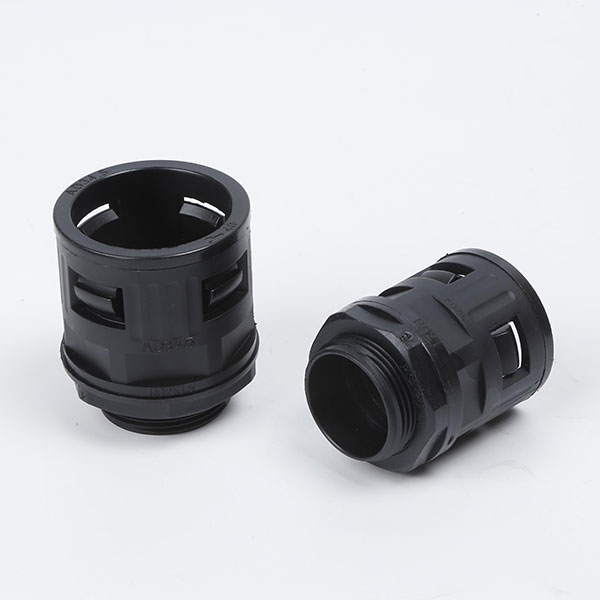
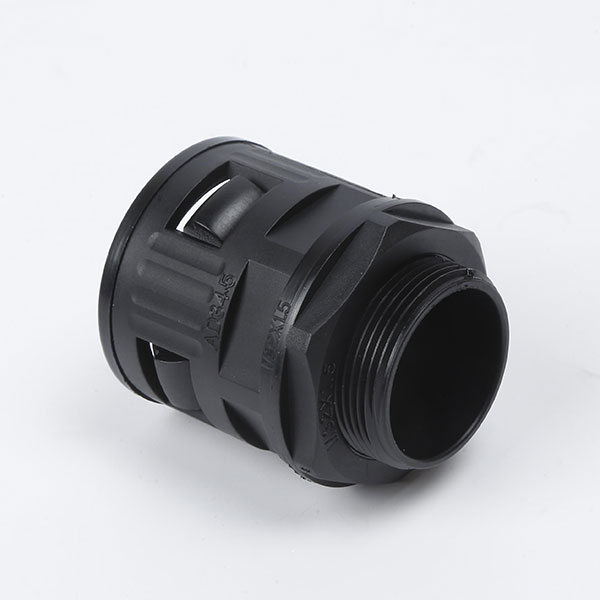
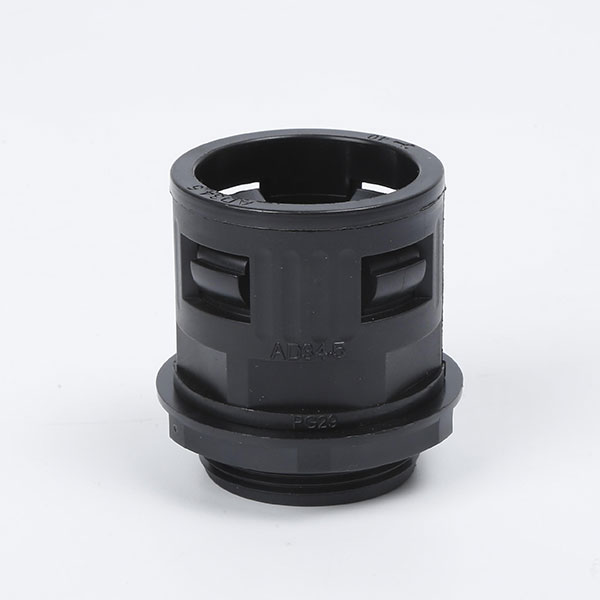
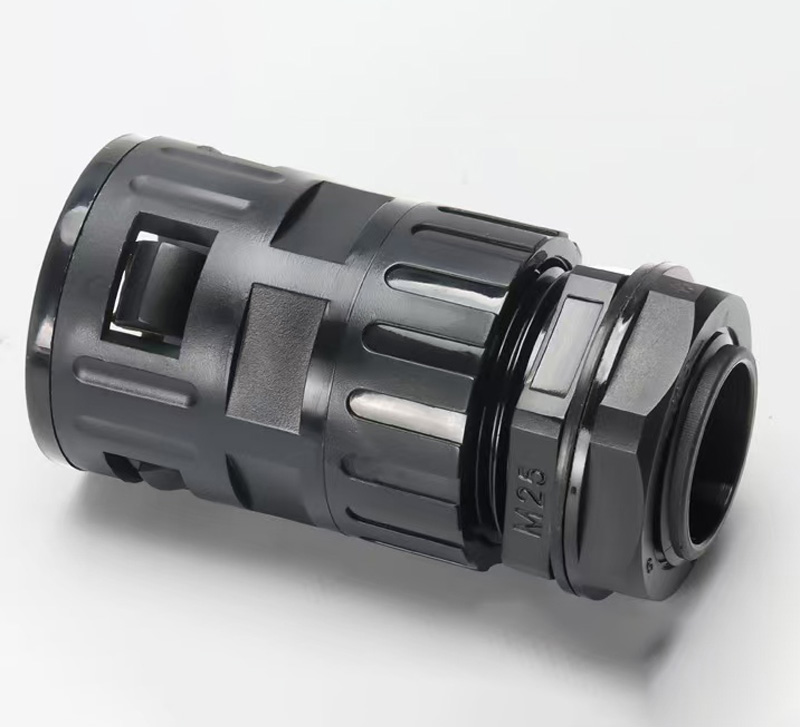
Corrugated Pipe Straight Connector usually have a simple and effective structural design, and one end can be directly inserted into the bellows to achieve a tight connection. Adopting the direct plug-in connection method, the corrugated pipe can be quickly inserted and the operation is convenient and fast. This connection method does not require complicated tool assistance and is very practical in some pipeline systems that require quick installation or disassembly. For example, when building temporary pipelines for hydraulic systems and pneumatic systems or repairing equipment, the connection or separation of bellows from other components can be quickly completed. The connection of the straight plug is relatively tight, which ensures that it will not loosen or leak easily when the pipeline transmits media. Whether it is transmitting hydraulic oil, compressed air, water or other chemical media, it can maintain a stable connection state.
Feature: The inner lock and body are specially designed, and only need to be removed and unplugged without tools.
Application: Can be adapted to different types of corrugated pipes, whether metal or plastic. At the same time, in different pipeline systems, such as hydraulic systems, pneumatic systems, water supply pipelines, chemical equipment pipelines, etc., as long as the specifications of the bellows match, they can be connected smoothly.